Back Emilia-Romagna Afrikaans Emilia-Romagna ALS ኤሚልያ-ሮማኛ Amharic Emilia-Romanya AN إميليا-رومانيا Arabic Emilia-Romaña AST Emiliya-Romanya Azerbaijani امیلیا-رومانیا AZB Émilia-Romagna BAN Emilia-Romagna BCL
This article's factual accuracy may be compromised due to out-of-date information. (April 2023) |
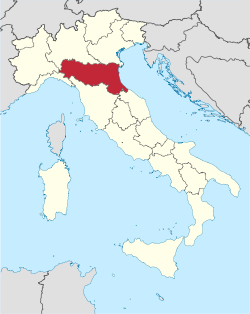
Emilia-Romagna
| |
|---|---|
|
| |
 | |
| Country | Italy |
| Capital | Bologna |
| Government | |
| • President | Stefano Bonaccini (PD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 22,446 km2 (8,666 sq mi) |
| Population (2010-11-30) | |
| • Total | 4,446,220 |
| • Density | 200/km2 (510/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | English: Emilia-Romagnan Emilian: Emigliàn (man) Emilian: Emiglièna (woman) Romagnol: Rumagnòl (man) Romagnol: Rumagnòla (woman) Italian: Emiliano (man) Italian: Emiliana (woman) or Italian: Romagnolo (man) Italian: Romagnola (woman) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | €163.293 billion (2021) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | IT-45 |
| NUTS Region | ITH[2] |
| HDI (2022) | 0.940[3] very high · 1st of 21 |
| Website | www |
Emilia-Romagna (UK: /ɪˌmiːliə roʊˈmɑːnjə/, US: /eɪˌmiːljə/, both also /ɛˌmiːljə -/;[4][5][6][7] Italian: [eˈmiːlja roˈmaɲɲa]; Emilian: Emégglia-Rumâgna or Emîlia-Rumâgna; Romagnol: Emélia-Rumâgna) is an administrative region of northern Italy, comprising the historical regions of Emilia and Romagna. Its capital is Bologna. It has an area of 22,446 km2 (8,666 sq mi), and a population of 4.4 million.
Emilia-Romagna is one of the wealthiest and most developed regions in Europe, with the third highest gross domestic product per capita in Italy,[8][9] Emilia-Romagna is also a cultural, economic and tourist center, being the home of the University of Bologna, the oldest university in the world;[10] containing Romanesque and Renaissance cities, such as Modena, Parma and Ferrara, and the once Western Roman Empire's capital city, Ravenna; encompassing eleven UNESCO heritage sites;[11] being a center for food and automobile production (home of automotive companies such as Ferrari, Lamborghini, Maserati, Pagani, De Tomaso, Dallara, and Ducati); and having popular coastal resorts such as Cervia, Cesenatico, Rimini and Riccione. In 2018, the Lonely Planet guide named Emilia-Romagna as the best place to see in Europe.[12] The region is home to the third largest community of foreign residents in the country, after Lombardy and Lazio.[13]
- ^ "Population on 1 January by age, sex and NUTS 2 region", www.ec.europa.eu
- ^ Commission Regulation (EU) 2016/2066 of 21 November 2016 amending the annexes to Regulation (EC) No 1059/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the establishment of a common classification of territorial units for statistics (NUTS)
- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ^ "Emilia-Romagna". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). HarperCollins. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
- ^ "Emilia-Romagna". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
- ^ "Emilia-Romagna". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 27 May 2022.
- ^ "Emilia-Romagna". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
- ^ Regional GDP per inhabitant in the EU27: GDP per inhabitant in 2005 ranged from 24% of the EU27 average in Nord-Est Romania to 303% in Inner London. European Commission, Eurostat. 12 February 2008.
- ^ "Qualita' della vita: il dossier". Il Sole 24 ORE. Retrieved 28 November 2013.
- ^ "Università di Bologna (oldest university in the world)". Virtual Globetrotting. 21 October 2006. Retrieved 28 November 2013.
- ^ "UNESCO SITES in Emilia Romagna". UNESCO SITES in Emilia Romagna. 16 February 2017. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- ^ Planet, Lonely. "10 best places to visit in Europe in 2019". Lonely Planet.
- ^ "Cittadini Stranieri in Italia - 2021". Tuttitalia.it (in Italian). Retrieved 19 December 2022.